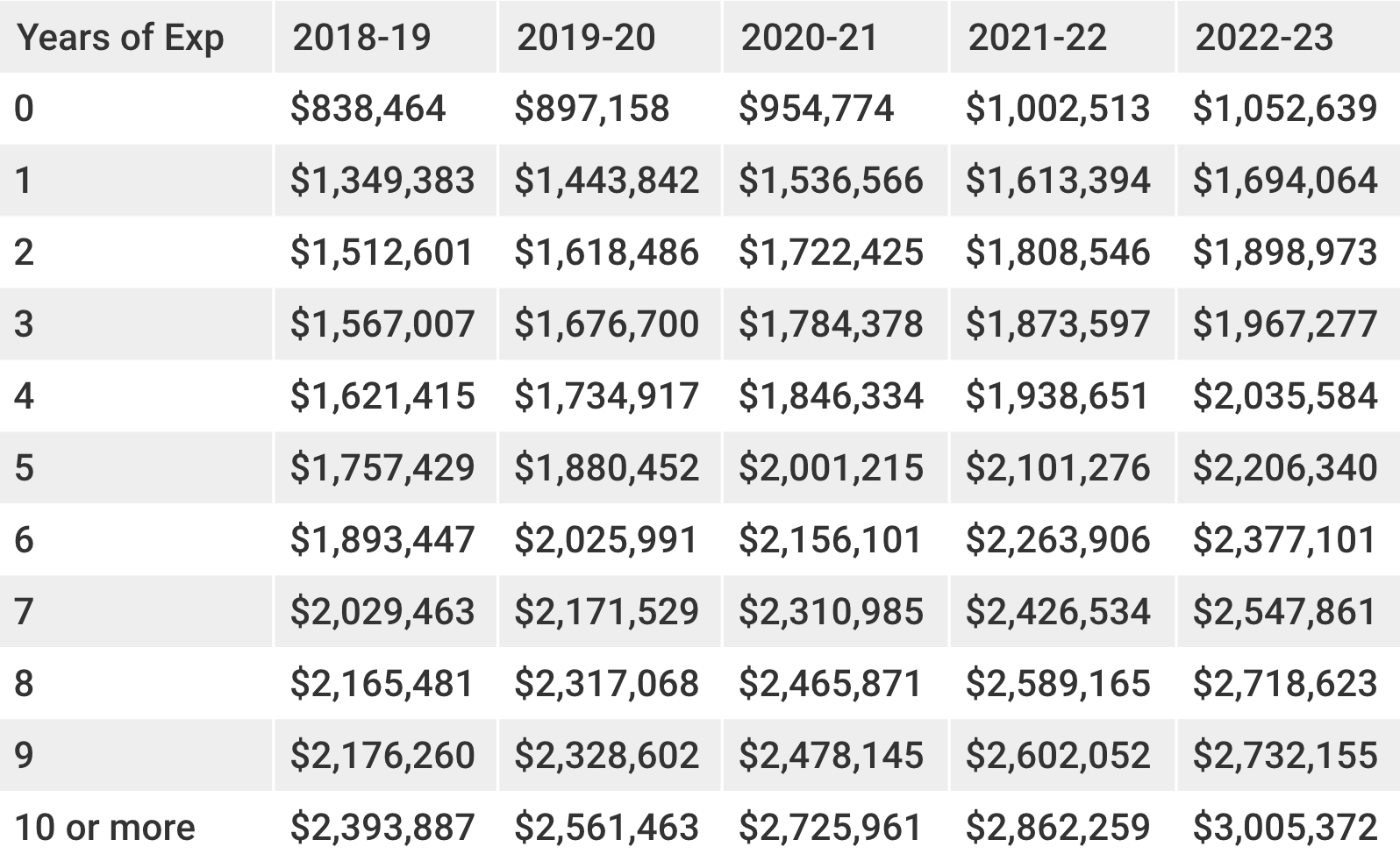
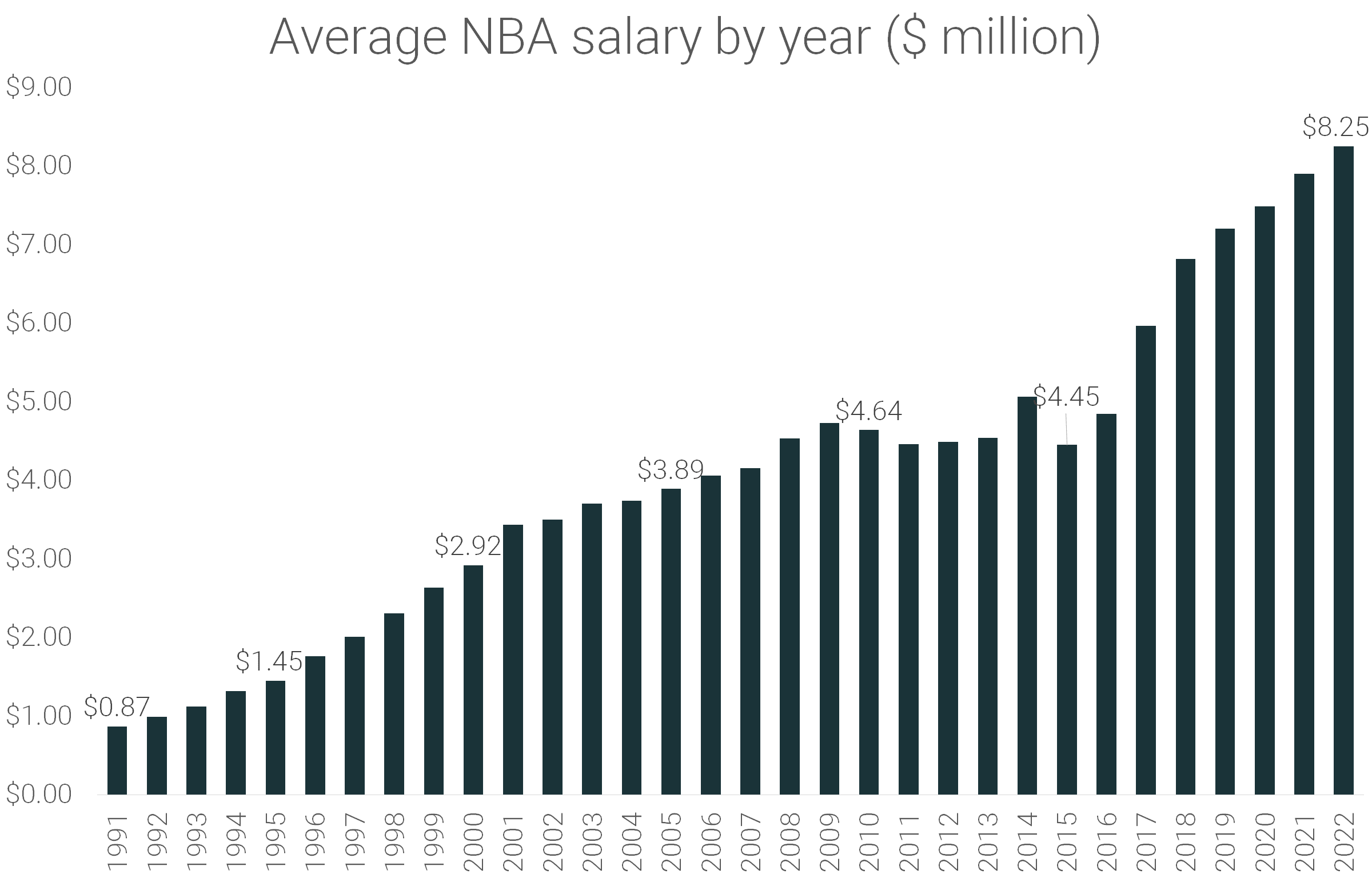
How does the base pay for NBA players influence their careers and the league's financial structure? Understanding the NBA's minimum salary is key to appreciating the league's economic landscape.
The base salary set for players entering the league, or for those under contract renegotiations, represents a crucial financial threshold. This figure serves as a foundational payment structure, outlining a minimum amount guaranteed to players. This minimum compensation plays a pivotal role in establishing the economic framework within the league and shaping the careers of its participants. Variations in this baseline salary reflect factors like the collective bargaining agreement, performance evaluations, and market dynamics.
This baseline pay structure is of significant importance to the league's overall stability. It affects the financial health of teams, influences player recruitment and retention strategies, and shapes the balance of power within the NBA ecosystem. Historically, fluctuations in this minimum salary have corresponded to shifts in the overall economic climate and changes in the league's financial priorities. These shifts impact the availability of talent and the competitiveness of different teams.
Moving forward, we will delve into the factors driving minimum salary changes and how these changes affect the players themselves, teams, and the NBA as a whole.
NBA Minimum Salary
The NBA minimum salary dictates the financial foundation for players, influencing team strategies and the overall health of the league. Understanding its key aspects is crucial for grasping the intricacies of professional basketball economics.
- Compensation
- Negotiation
- Contract
- CBA Impact
- Team Balance
- Player Recruitment
- Economic Factors
The minimum salary, a contractual element, reflects economic realities and the Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA). Negotiations determine the amount, impacting team spending and player recruitment. A higher minimum often necessitates more balanced rosters, as teams must adhere to salary caps. Economic downturns can influence this minimum, requiring adjustments to ensure player compensation remains competitive. The minimum salary, in effect, acts as a crucial component of the CBA, safeguarding a baseline of income for new and established players, while teams consider how these factors influence recruitment strategies and roster management. For instance, a significantly higher minimum salary might incentivize teams to prioritize youth development, while a lower minimum could make free-agent acquisition more attractive. These considerations highlight the multifaceted interaction between the minimum salary and the overall health of the NBA ecosystem.
1. Compensation
Compensation in the NBA is intricately linked to the minimum salary. The minimum salary establishes a baseline for player earnings, influencing negotiations and the overall structure of salaries throughout the league. Understanding this connection is essential to comprehending the financial dynamics within the NBA.
- Impact on New Entrants
The minimum salary directly affects rookie compensation, serving as a crucial entry point into the league. It sets a floor for rookie contracts, influencing the compensation structure and potentially affecting the pool of talent available to teams. Teams often factor the minimum salary into their overall salary cap strategies when considering the addition of new players, especially rookies.
- Role in Contract Negotiations
The minimum salary acts as a benchmark in contract negotiations. Players and teams often use it as a reference point, influencing considerations surrounding performance-based bonuses, signing bonuses, and other supplementary compensation elements. The minimum salary provides a baseline for comparison, affecting negotiations and salary structures across all levels of experience in the NBA.
- Influence on Team Spending
The minimum salary, along with associated rules and regulations, influences team spending decisions. Teams must balance the needs of their existing players and the desire to attract new talent while remaining within the constraints of the salary cap and the stipulated minimum. The minimum salary framework directly impacts how teams strategize around acquiring talent and building a competitive roster.
- Influence on Player Career Trajectories
The minimum salary framework plays a role in shaping career paths. Players entering the league with a certain skillset or playing role may find their compensation influenced significantly by the minimum salary, influencing their opportunities for advancement or their decision-making about career paths. Furthermore, players with significant past experience may negotiate their compensation to account for differences from the established minimum.
In conclusion, the NBA minimum salary significantly impacts player compensation across the league. This establishes a critical benchmark impacting everything from rookie contracts to long-term negotiations, further influencing how teams manage their financial resources and plan for future roster construction.
2. Negotiation
Negotiation plays a crucial role in determining the NBA minimum salary. The minimum salary isn't a fixed figure; it's a product of ongoing negotiation between players' representatives, team management, and the league's governing body. The specific details of each player's contract, often influenced by performance expectations and market value, intertwine with the agreed-upon minimum compensation. The CBA's framework dictates the process and parameters of these negotiations, which fundamentally shape the financial structure of the league. Variations in player skill sets and market demand directly impact the strategies employed during negotiations concerning the minimum salary.
Real-world examples illustrate this dynamic interplay. A strong performance by a rookie during the preseason might influence a team's negotiation strategy for their contract, potentially pushing their compensation above the minimum salary. Conversely, a player with a history of underperformance might find negotiations centered around the minimum to maintain budgetary control. The minimum salary acts as a critical reference point in these negotiations, influencing the overall balance between player compensation and team budgets. The influence of the CBA, encompassing provisions for minimum salary increases and adjustments, emphasizes the collective bargaining aspect of these negotiations, further highlighting their profound importance for the league's financial integrity.
Understanding the negotiation process surrounding the NBA minimum salary is essential for appreciating the intricate economic factors shaping the league. The dynamic relationship between players, teams, and the league's governing bodies ensures the competitiveness of the league while maintaining financial sustainability. Fluctuations in the minimum salary, driven by negotiation outcomes, reflect broader economic trends and the evolving dynamics of the professional basketball market. The insights gained from studying these negotiations provide a comprehensive understanding of the intricate connections within the NBA's economic ecosystem. Ultimately, the negotiation process surrounding the minimum salary underscores the complex interplay between player compensation, team budgets, and the health of the league as a whole.
3. Contract
Contracts are fundamental to the NBA minimum salary. A contract defines the terms of employment, including compensation. The minimum salary, established through collective bargaining, forms the baseline compensation within a contract for players. This minimum establishes a floor for entry-level and renegotiated contracts. Consequently, contracts serve as the embodiment of the minimum salary, outlining the guaranteed financial obligations for players. Variations in contract length, incentives, and performance-based bonuses, all within the framework of the minimum salary, illustrate this connection. For instance, a rookie contract will often be structured around a base salary, potentially exceeding the minimum but still adhering to its established parameters. Similarly, contracts for experienced players might incorporate a minimum salary as a starting point, with potential adjustments contingent on performance, but anchored by the established base.
The NBA's minimum salary, enshrined within contracts, directly influences player acquisition and roster management strategies. Teams must adhere to the salary cap and the minimum, impacting their ability to sign players. Contracts incorporating the minimum salary must align with established league guidelines, ensuring compliance with the collective bargaining agreement. This alignment is crucial for maintaining the league's financial equilibrium and ensuring equitable compensation. A team exceeding the salary cap or failing to meet the minimum salary stipulations faces penalties. Understanding the role contracts play in guaranteeing the minimum salary illuminates the financial and structural mechanisms that sustain the league.
In summary, contracts are the operational manifestation of the NBA minimum salary. They represent the agreed-upon compensation, stipulating the baseline payment, and shaping the league's financial ecosystem. Contracts serve as the legal framework for minimum salary obligations, ensuring financial stability and adherence to the agreed-upon compensation structure within the NBA. This framework ensures that every player, regardless of experience, receives a minimum level of guaranteed compensation, maintaining the league's overall structure and competitiveness.
4. CBA Impact
The Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA) profoundly influences the NBA minimum salary. The CBA, a legally binding contract between the league and the players' association, dictates the terms and conditions under which players are compensated, including the minimum salary. This agreement establishes the framework for financial stability and competitiveness within the league, affecting how teams structure their rosters and salaries. Its impact extends beyond the minimum salary to encompass various facets of the NBA's economic landscape.
- Minimum Salary Determination
The CBA directly establishes the minimum salary. It outlines the parameters for salary negotiation, including factors such as the salary floor and any potential adjustments based on factors like economic conditions or league performance. The CBA provisions define how the minimum salary is calculated, updated, and enforced, impacting every player's income at the entry level and during renegotiations.
- Salary Cap and its Relationship
The CBA establishes the salary cap, a crucial element impacting the minimum salary. The interplay between the minimum salary and the salary cap is paramount in determining player compensation. A higher minimum salary often necessitates a higher salary cap to maintain a balanced financial structure, and this relationship reflects the broader economic climate. The CBA ensures the cap doesn't fall below a defined value relative to the minimum.
- Economic Adjustments and Minimum Salary Changes
Economic conditions can necessitate CBA adjustments affecting the minimum salary. During periods of economic uncertainty or high inflation, the CBA might mandate alterations to the minimum salary to ensure competitive compensation. These revisions, outlined in the agreement, directly address and reflect economic conditions in setting the appropriate minimum salary floor for the league.
- Player Compensation Structure and its impact
The CBA establishes the framework for player compensation structures beyond the minimum salary. It details aspects like performance-based bonuses, signing bonuses, and other considerations that can fall within a range but are often tied to the minimum, thus impacting compensation patterns throughout the league. The CBA is fundamental to defining the various levels of compensation across player experience, which directly correlate with the minimum.
In conclusion, the CBA serves as the fundamental governing document influencing the NBA minimum salary. Through its stipulations on the minimum and its relationship to other financial metrics like the salary cap, the CBA shapes the league's economic landscape, ensuring stability and competitiveness within the league. Variations in the CBA directly impact the minimum, demonstrating the profound connection between the rules and conditions of the league, player compensation, and the overall financial well-being of the NBA.
5. Team Balance
Team balance, a crucial element in NBA success, is intrinsically linked to the minimum salary. The minimum sets a baseline compensation, impacting a team's ability to assemble a balanced roster. Teams aiming for competitive parity must navigate the constraints of the minimum salary when building a squad. Failure to maintain a balanced team can lead to significant disadvantages, reflected in performance and potential financial difficulties.
Teams aiming for balance must carefully consider the minimum salary when constructing their rosters. A roster heavily skewed towards highly compensated players might leave limited funds to recruit and retain less expensive but valuable players. This imbalance, driven by the necessity to adhere to the salary cap while meeting the minimum, can result in insufficient depth at various positions. A team with significant talent at a few critical positions but lacking depth at others becomes vulnerable. Conversely, a roster evenly distributed across positions can better withstand injuries, manage different playing styles, and maintain competitiveness throughout a season. The minimum salary, therefore, acts as a catalyst for roster composition. For instance, a team exceeding the luxury tax threshold might be limited to prioritizing players under the minimum salary cap to ensure roster balance. This strategy directly illustrates the interplay between team balance, the minimum salary, and financial constraints.
Understanding the link between team balance and the minimum salary is critical for strategic roster management. Teams that effectively navigate these constraints are better positioned to maintain competitive rosters. Failing to recognize these connections can lead to roster imbalances, affecting team performance and the long-term financial viability of the franchise. The minimum salary's significance in influencing roster decisions underscores the importance of strategic planning and financial foresight in maintaining sustainable and competitive NBA teams.
6. Player Recruitment
Player recruitment within the NBA is intricately linked to the minimum salary. The minimum salary acts as a critical threshold, influencing the pool of available talent and shaping recruitment strategies. Teams must meticulously consider the minimum salary when evaluating prospective players, weighing their skill level against the budgetary constraints imposed by this baseline compensation. Recruitment decisions are not merely about acquiring talent; they are also about managing financial resources within the confines of the salary cap and the minimum salary. Teams strategically prioritize players whose projected contributions align with the financial limitations established by the minimum salary.
The minimum salary often affects a team's ability to attract high-profile players. A high minimum might restrict a team's capacity to sign free agents or retain established players who command substantial salaries. This can compel teams to focus on draft prospects or players who demonstrate strong value at or near the minimum salary level. For instance, teams might favor drafting high-potential rookies with the understanding that their salaries will be capped within the minimum framework. This strategy emphasizes long-term value over immediate impact. Conversely, a lower minimum salary might open up opportunities for teams to secure established players whose salary demands fall within the budget. The minimum salary thus directly impacts the types of players a team can attract and the recruitment strategies they employ.
A thorough understanding of the connection between player recruitment and the minimum salary is essential for NBA front offices. This understanding enables proactive planning and informed decision-making, optimizing roster construction and financial management. Teams need to assess the long-term costs of recruitment, weighing the potential of players against their projected salary expectations within the context of the minimum salary and salary cap. This awareness allows teams to strategize for both short-term and long-term success within the NBA's complex financial framework. Ultimately, a keen understanding of this dynamic allows teams to build a competitive roster, maximizing the value of every player while adhering to the financial parameters set by the minimum salary.
7. Economic Factors
Economic factors exert a profound influence on the NBA minimum salary. Fluctuations in economic conditions directly impact the financial stability of teams, the compensation players receive, and the overall competitiveness of the league. Understanding these economic forces is crucial for comprehending the dynamic nature of the NBA's salary structure and its impact on player recruitment, team strategies, and the league's financial health.
- Inflationary Pressures
Inflationary pressures directly affect the minimum salary. As prices for goods and services increase, the minimum salary must adjust to maintain a relative level of purchasing power. Failure to adjust the minimum salary can erode the real value of player compensation, impacting player motivation and potentially discouraging new talent. Historical data on inflation and corresponding minimum salary adjustments demonstrate the correlation between these economic factors. If the minimum salary does not keep pace with inflation, players' real income will decrease, potentially hindering the league's ability to attract and retain top talent.
- Economic Recessions
Economic downturns can influence the minimum salary. During recessions, reduced consumer spending and business activity often lead to decreased team revenue. This can necessitate a more conservative approach to player compensation, potentially resulting in a lower minimum salary. Conversely, periods of economic growth can lead to increased team revenue, potentially justifying higher minimum salaries.
- Labor Market Conditions
The broader labor market influences the minimum salary. If demand for similar athletic talent in other industries rises, it might require an upward adjustment to the minimum salary to remain competitive. Conversely, a decrease in demand for similar professions could allow the minimum salary to remain stable or even decline slightly. This demonstrates how outside economic factors can influence a sport's compensation structure.
- League Performance and Revenue Streams
The success and profitability of the NBA, and its revenue streams, impact the minimum salary. A highly successful season, often reflected in increased ticket sales, merchandise revenue, and television viewership, might justify a higher minimum salary. Conversely, a downturn in league performance can lead to pressure on teams to reduce costs, potentially impacting the minimum salary. The relationship between team financial health and the minimum salary is crucial for maintaining the league's economic stability.
In conclusion, economic factors consistently intertwine with the NBA's minimum salary. From inflationary pressures to recessions, labor market conditions, and league performance, these factors influence player compensation and the overall financial health of teams and the league. Understanding these connections is key for analyzing the dynamic interplay within the NBA's economic ecosystem and anticipating potential adjustments to the minimum salary in response to changing economic realities. This understanding further contextualizes the complex negotiation process involved in determining the minimum salary.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common inquiries regarding the NBA minimum salary, providing clarity on its determination, impact, and related factors.
Question 1: What is the current NBA minimum salary?
The current minimum salary is a dynamic figure, subject to annual adjustments based on the Collective Bargaining Agreement (CBA) and economic considerations. Consult the most recent CBA for the precise current amount.
Question 2: How is the minimum salary determined?
The minimum salary is a product of negotiations between the National Basketball Players Association (NBPA) and the NBA. These negotiations take into account economic factors, market conditions, and the overall financial health of the league, resulting in a figure deemed fair and sustainable.
Question 3: How does the minimum salary impact rookie contracts?
Rookie contracts often incorporate the minimum salary as a baseline. Negotiations surrounding these contracts may result in figures exceeding the minimum, depending on the player's potential and draft position. The minimum still provides a critical financial foundation for entry-level players.
Question 4: What role does the salary cap play in relation to the minimum salary?
The salary cap and the minimum salary are interconnected. Teams must adhere to the salary cap while ensuring compensation for all players meets or exceeds the minimum. This interplay influences roster construction strategies and influences the available talent pool.
Question 5: How do economic factors influence the minimum salary?
Economic conditions, such as inflation, influence the minimum salary's adjustment. The CBA often includes provisions for adjusting the minimum salary to reflect economic realities, preventing significant erosion of player purchasing power.
In summary, the NBA minimum salary is a dynamic element within the league's financial structure, shaped by negotiation, economic conditions, and the overall financial health of the NBA. Understanding these factors is crucial to grasping the complexities of player compensation and team management within the league.
Moving forward, we will explore the historical context of the minimum salary and its evolution over time.
Conclusion
The NBA minimum salary, a cornerstone of the league's financial framework, profoundly influences player compensation, team strategies, and the overall economic health of the professional basketball landscape. This study has explored the multifaceted nature of this critical figure, examining its determination through collective bargaining, its impact on rookie contracts and veteran negotiations, and its intricate relationship with the salary cap. The analysis further highlighted the crucial role of economic factors, such as inflation and recessions, in shaping the minimum salary's trajectory. Understanding this dynamic reveals how the minimum salary directly influences player recruitment, roster management, and team balance, ultimately impacting the league's competitiveness and sustainability. The interconnectedness of these factors underscores the complexity of maintaining a balanced and thriving professional basketball league.
The NBA's minimum salary, a dynamic component, reflects the evolving economic and competitive realities of the sports industry. Maintaining its relevance necessitates ongoing adaptation and responsive adjustments to ensure fair compensation for players, sustainable team operations, and the long-term health of the NBA. Future research should focus on analyzing specific instances where the minimum salary has significantly impacted team strategies, player career trajectories, or the overall league performance. By continuing to examine this complex issue, a deeper understanding of the NBA's economic model can be achieved, contributing to the ongoing discussion about the balance between player compensation and league profitability.
- Bill Hemmer Salary Net Worth Fox News Anchors Journey
- Where Are The Bones Cast Now Relationships More Revealed